Installation
Intruction
Install on Linux
Install on Kubernetes
Related Tools
Cluster Operation
Quick Start
Cluster Admin Guide
Multi-tenant Management
Platform Management
Infrastructure
Monitoring Center
User Guide
Storage
Configuration Center
Project Settings
Development Guide
API Documentation
Overview of Multi-tenant Management
The core of multi-tenancy is to allocate the authority relationship between different users and resources. For the container management platform, the main resources are computing resources, storage resources and network resources, which are also the key object resources of KubeSphere multi-tenany.
In the KubeSphere multi-tenancy system, resources are divided into three levels:
- Cluster
- Workspace
- Project and DevOps project
Resources at different levels can be flexibly customized to divide users' permission scope, which is used to achieve resource isolation between different users.
Authority Management Model
Common permission management models include ACL, DAC, MAC, RBAC and ABAC. In KubeSphere, we make use of the RBAC authority management model to control users' authority. Users don't need to directly associate with resources, but carry out authority control through role definition.
Resource Hierarchy
Cluster
Clustering refers to the current Kubernetes cluster, which provides computing, storage, and network resources for tenants. workspaces can be created under a cluster.
Workspaces
Under a cluster, you can create workspaces to manage different projects in groups. Projects and DevOps projects can be created in workspaces.
Projects and DevOps projects
Projects, DevOps projects are the minimum level of version permission management, consuming the resources of the cluster to deploy and build applications.
Multi-level Permission Control
Cluster permission control
Cluster roles define user control over cluster resources, such as nodes, monitoring, accounts, and so on.
Workspaces permission control
The workspaces role defines the user's control authority over projects and projects in the workspaces and the management authority of workspaces members.
Project and project permission control
Creators of projects and projects can share their projects with other users by inviting members, giving different members different roles and differentiating permissions.
IAM Architecture
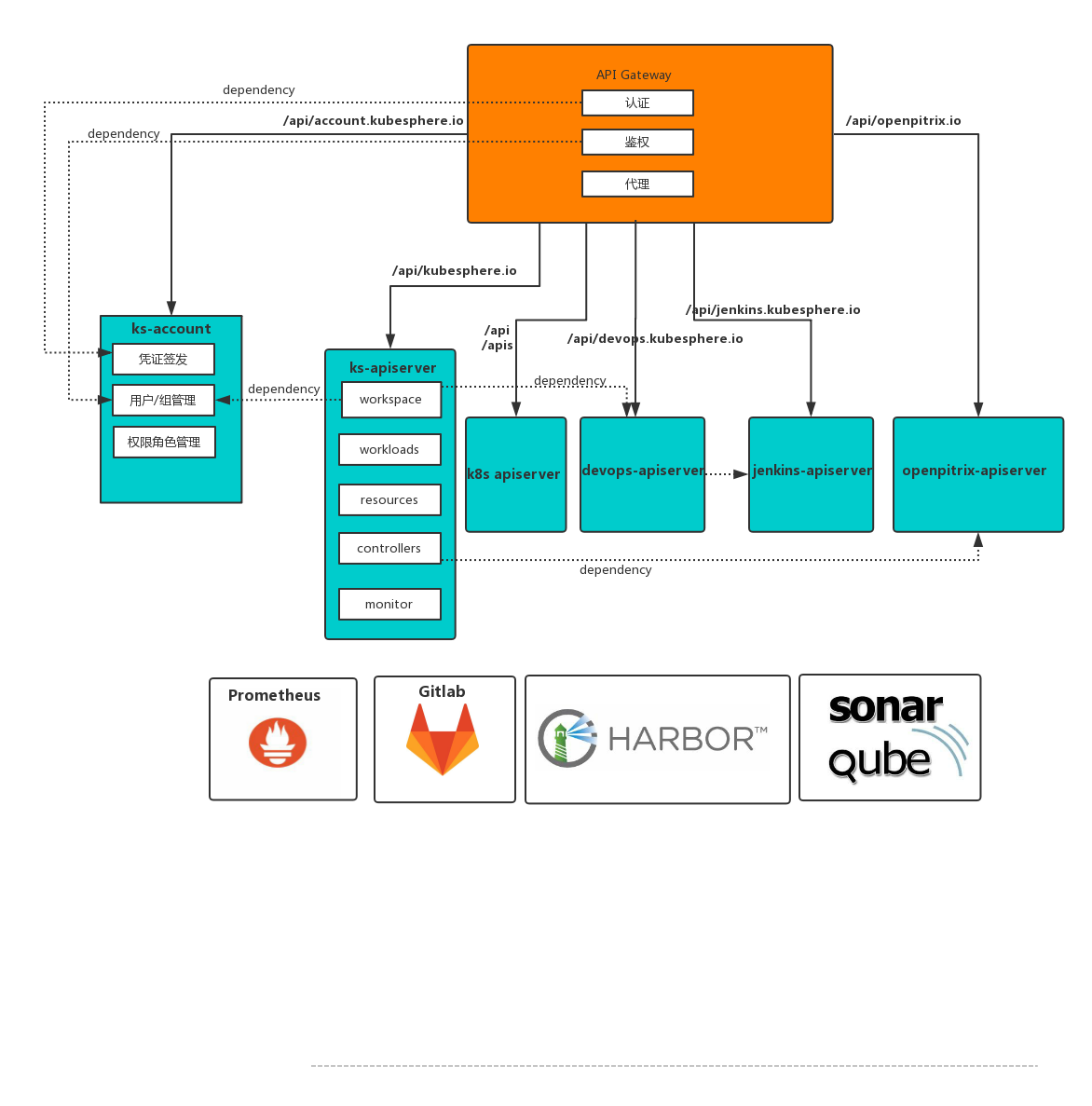
Details
In familiar and understand the resource hierarchy, permissions management way, to taichung every level administrators and ordinary users, understand the meaning of each grade of concrete members and roles, how to better management platform, the role of members and is the key links of actual use, please continue to refer to the role authorization overview.